PEO vs HRO Explained: Pros, Cons, and Key Differences
Navigating the complexities of workforce management can be challenging for any business.
As companies strive to streamline operations and enhance efficiency, understanding the difference between Professional Employer Organizations (PEOs) and Human Resource Outsourcing (HRO) becomes crucial.
This article breaks down what PEO and HRO are, the services they offer, and their key differences.
It also explores the advantages and disadvantages of choosing a PEO, helping you decide which option best fits your business needs.
What Is PEO and Its Pros and Cons?
A Professional Employer Organization (PEO) is a company that offers HR services for small and medium-sized businesses. They handle tasks like payroll, managing employee benefits, following labor laws, managing risks, and ensuring legal compliance.
By working together, PEOs help companies share employee management responsibilities, making tasks easier and improving processes. employee retention and employee engagement.
What Services Does a PEO Offer for Business Growth?
PEOs provide many services to simplify HR tasks for businesses, such as managing payroll, administering benefits, and organizing employee training programs to improve employee involvement and happiness.
These organizations excel in payroll processing, ensuring accuracy and timeliness while minimizing administrative burdens for businesses.
Besides standard payroll services, PEOs provide full benefits packages like those of large companies, which helps small businesses bring in employees and improve. employee satisfaction.
Besides this, help with compliance is an essential service. It helps clients understand and deal with complicated employment laws and rules, reducing the chance of expensive fines.
By helping in recruitment, these partnerships allow businesses to find and hire qualified candidates quickly, improving talent acquisition strategies.
Employee training programs improve how work is done by providing workers with important skills, supporting ongoing professional growth, and helping save money, thereby enhancing performance management.
What Is HRO and Its Service Model?
Human Resource Outsourcing (HRO) involves businesses hiring another company to manage specific HR duties. This allows businesses to concentrate on their core operations while ensuring tasks such as payroll, recruitment, and employee benefits are handled properly and quickly, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
What Services Does an HRO Offer for Scalability?
An HRO usually offers services like handling payroll, managing rules and regulations, organizing activities to keep employees motivated, and finding new employees, all customized to fit the unique requirements of their client companies, ensuring effective vendor management.
By simplifying office tasks, these organizations can handle important payroll services to make sure employees get their pay on time and correctly, which helps. financial management.
Compliance support helps businesses understand and follow complicated rules, lowering the chance of expensive fines.
Effective hiring practices help HR officers find talented individuals who enhance the workplace and boost productivity, fostering a positive environment. organizational culture.
These services help improve employee satisfaction since teams feel appreciated and supported. They also make operations run more smoothly, letting organizations concentrate on their main goals instead of administrative tasks, contributing to business continuity.
What Are the Key Differences Between PEO and HRO in Terms of Service Customization?
Knowing the main differences between a PEO and an HRO is important for businesses wanting to improve their HR functions and achieve a competitive advantage.
Though both offer HR services, they work differently: a PEO involves sharing employment responsibilities and employee leasing, while an HRO mainly outsources specific HR tasks without sharing employment roles, impacting employer responsibilities.
PEO vs HRO Comparison Statistics
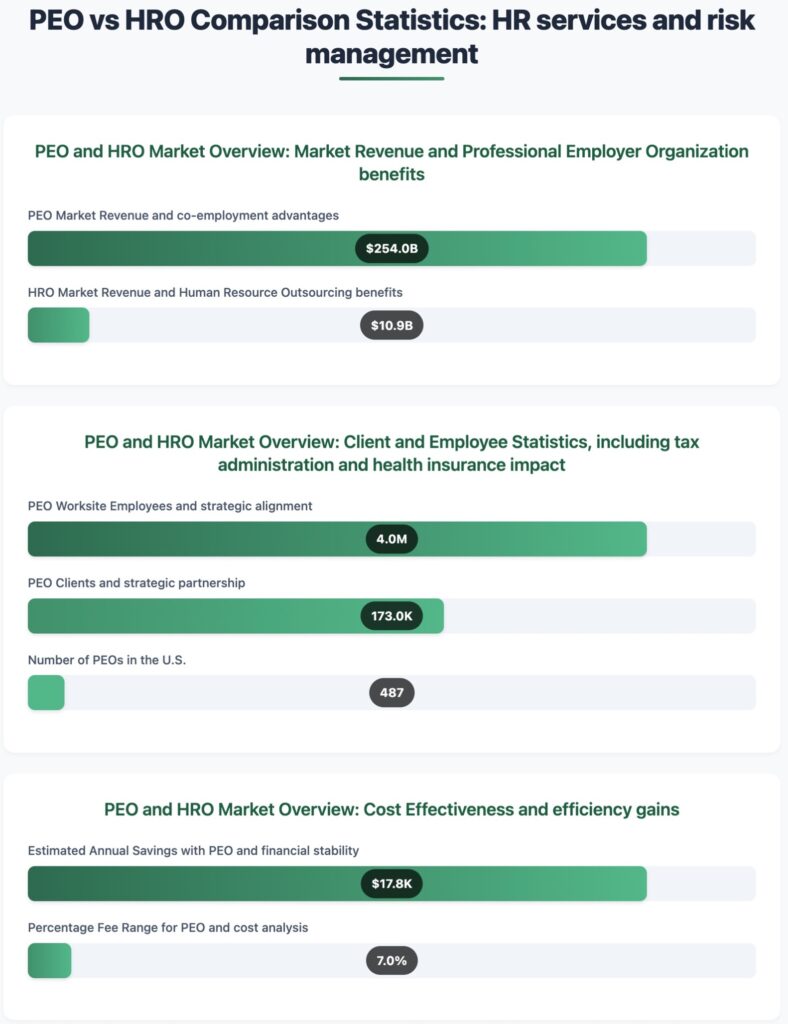
The PEO vs HRO Comparison Statistics offers a detailed look into the Professional Employer Organization (PEO) and Human Resource Outsourcing (HRO) markets, focusing on revenue, client and employee statistics, and cost-effectiveness. This data offers information on the size, operational risks, and economic advantages of these HR solutions.
PEO and HRO Market Overview highlights significant differences in market revenue. The PEO market revenue is a noteworthy $254 billion, far surpassing the $10.9 billion revenue of the HRO market. This difference shows the wider range and combination of services provided by PEOs, which handle all HR tasks, such as payroll, benefits, and compliance for client businesses.
- Client and Employee Statistics: There are 487 PEOs in the U.S., serving 173,000 clients and managing 4 million worksite employees. These figures indicate the extensive reach and influence of PEOs in managing employee-related functions, allowing companies to focus on their core business operations.
- Cost Effectiveness: Engaging with a PEO can lead to estimated annual savings of $17,750 for businesses, highlighting the financial benefits of outsourcing HR functions. Moreover, the percentage fee range for PEO services is 7%, which is often offset by the savings in administrative and compliance costs.
In summary, the PEO vs HRO Comparison Statistics highlights the strong position of PEOs in the HR outsourcing market because of their complete range of services, agreements on service levels, and ability to save money. PEOs provide an effective HR management and operational solution for businesses, thanks to their strong revenue and wide client and employee involvement.
1. Employment Relationship
The employment relationship is one of the most significant distinctions between a PEO and an HRO; a PEO establishes a co-employment relationship with clients, sharing responsibilities for employee management, while HROs typically do not engage in such arrangements and focus on outsourcing specific HR functions, like recruitment process outsourcing and benefits administration.
This co-employment arrangement lets companies improve their employee leasing abilities, creating a cooperative setting where both the PEO and the client share important human resource duties, enhancing employee relations and adherence to industry standards.
Employers can gain from the PEO’s knowledge in following rules, handling risks, making administrative tasks easier, and improving employee benefit plans.
This model can create problems, such as confusion over shared duties and who among the staff is accountable.
Unlike HROs, which make HR processes simpler and fit specific business demands, they might not offer the strong employee involvement and alignment with company culture that co-employment can give.
2. Legal Liability
In terms of legal liability, PEOs assume shared responsibility for compliance with labor laws and regulations, potentially reducing the risk for client businesses, while HROs often have limited liability in comparison, focusing mainly on the services provided.
This difference is very important in how these organizations handle risk and deal with possible legal problems. PEOs handle payroll and employee benefits, ensuring compliance with employment laws. This helps protect both workers and companies from legal problems.
Unlike HROs, which focus on specific tasks like hiring or teaching, they usually do not handle compliance checks. So, companies using their services need to make sure they follow labor laws themselves.
As a result, businesses opting for PEO arrangements might experience less liability exposure compared to those relying solely on HROs, who maintain greater responsibility for managing their HR functions without the added layer of shared liability.
3. Cost Structure
PEOs typically charge a fee per employee, covering a range of HR duties, which makes them a cost-effective choice for companies wanting full services. In contrast, HROs generally have flexible rates depending on the specific services a company requires.
This flexibility allows companies to tailor their HR expenditures according to their unique needs, potentially leading to significant savings over time.
When companies grow, the fixed costs of PEOs can make budgeting and financial planning easier, offering a consistent basis for planning expansion.
Conversely, businesses that opt for HROs can strategically select only the essential services they require, which may lead to cost efficiencies, especially for smaller businesses with limited HR requirements.
In the end, choosing between these options depends on the business’s goals and structure. It’s important to look closely at both short-term and long-term financial effects.
4. HR Responsibilities
HR responsibilities differ significantly between PEOs and HROs; PEOs take on a broader range of HR functions including employee engagement and benefits administration, while HROs focus on specific outsourced tasks such as payroll processing and compliance.
This distinction influences how employee satisfaction is nurtured and how smooth workflows are experienced within organizations.
For example, PEOs usually get involved directly by including employee training programs and encouraging a good workplace atmosphere, which increases involvement and commitment among employees.
HROs arrange tasks by ensuring essential administrative work is completed accurately and promptly, allowing companies to focus more on their primary business activities.
Providing targeted support for each model helps improve employees’ work life, leading to higher performance and less turnover.
What Are the Pros of Using a PEO?
One of the key advantages of engaging with PEOs is their capacity to integrate HR technology and data privacy measures, ensuring compliance and efficiency in handling human resources management tasks.
Using a PEO helps companies save money by sharing services and making operations easier. It provides HR knowledge that the company might not have, and provides employee benefit packages that increase employee retention and satisfaction; for instance, selecting the best PEO for health insurance can significantly enhance employee well-being and loyalty.
1. Cost Savings
A strategic business partnership with a PEO can significantly reduce outsourcing costs and labor costs, freeing up resources for core business operations and strategic planning.
One of the main advantages of working with a PEO is saving money. Companies can take advantage of the PEO’s larger scale to lower expenses for human resources tasks, employee benefits, and legal matters.
These organizations often negotiate better rates for health insurance and retirement plans, extending affordable benefits packages that small businesses would struggle to secure on their own.
For instance, a company might find itself paying significantly lower premiums due to the collective bargaining power of the PEO, which can lead to substantial savings on labor costs.
Companies can improve efficiency by hiring a PEO to handle HR tasks, allowing them to concentrate on key business areas. This operational efficiency increases productivity and allows employers to redirect money toward growth projects, which helps improve profits.
2. Access to Expertise
By using consulting services provided by PEOs, companies gain access to expert knowledge in managing employees and analyzing workforce data.
By working with a PEO, businesses receive HR support that helps with planning, following rules, and hiring the right people.
This helpful resource allows companies to understand and follow labor laws and regulations, helping them stay compliant and prevent expensive fines.
The recruitment efforts benefit significantly from specialized knowledge of industry trends and effective hiring strategies, helping organizations attract and retain top talent.
A PEO helps create good HR policies, which keeps operations running smoothly and supports a positive workplace environment.
Therefore, using such HR knowledge is very important for businesses that want to improve their HR strategy and reach long-term success.
3. Risk Management
Using PEO services can improve how risks are evaluated and help follow employee rights and financial duties more effectively.
PEOs help businesses with risk management by offering support in following labor laws, keeping employees safe, and reducing legal risks.
Working with a Professional Employer Organization allows businesses to get detailed checks that find possible issues in their human resources procedures.
These audits identify parts of the organization that might lead to risks and provide specific advice to better match industry rules.
PEOs create employee safety programs to promote a safe workplace, decrease the chance of accidents, and reduce workers’ compensation claims.
Using these strategies protects employees and greatly reduces the chances of expensive legal issues, allowing businesses to concentrate their resources on expanding and creating new ideas.
What Are the Cons of Using a PEO?
Despite the benefits, potential drawbacks include issues related to flexibility, potential conflicts of interest, and the need for clear contractual obligations.
Though working with a PEO offers many benefits, there are some potential drawbacks to think about.
These include:
- Losing some control over HR tasks
- Limited ways to tailor services
- Potential conflicts of interest

1. Loss of Control
Companies might experience a loss of control over employee classification and day-to-day human resources management tasks, affecting employee turnover and performance metrics.
Working with a PEO can sometimes mean losing control over HR tasks, which might make it hard to make decisions about employee interactions and the company culture.
When companies hand over these important tasks to an outside partner, they might find it hard to keep a steady message and method with their staff, which can end up impacting how motivated and productive employees are.
Not having clear control over HR policies can lead to differences in employee treatment or management, causing dissatisfaction and distrust. It is important for organizations to create a balanced working relationship with a PEO.
This helps them use the PEO’s knowledge while still having enough control over main HR strategies to match their own company values and goals.
2. Limited Customization
Another drawback is the limited customization of HR services offered by PEOs, which may not perfectly align with the unique needs of certain businesses, potentially hindering flexibility and responsiveness.
For companies with unique human resource needs or different company cultures, this rigid approach can create major problems, affecting employee productivity and work-life balance.
If a business doesn’t adjust its PEO services to match its unique way of working, employees might feel disconnected and unhappy, impacting customer satisfaction and employee productivity.
This limitation can stop a company from quickly responding to market changes or internal shifts, which is important for staying competitive in market competition.
This can impact how employees feel and their willingness to stay, as more workers look for places that match their values and where they receive individual attention, highlighting the importance of a strong value proposition and business strategy.
3. Potential Conflicts of Interest in Outsourcing Strategy
Working with a PEO can sometimes cause conflicts of interest, particularly in handling vendors and following laws, which can create problems in meeting legal requirements and affect labor relations.
When these conflicts surface, they can undermine the trust between the PEO and its clients, posing risks to overall business integrity. This change might affect relationships with outside vendors, especially if the PEO favors certain suppliers, which could reduce competition and increase costs.
The ambiguity in compliance responsibilities can result in regulatory setbacks that could jeopardize the client’s standing. To mitigate these risks, it is essential that clear and concise service level agreements (SLAs) are established, outlining the expectations, responsibilities, and performance metrics for all parties involved.
This approach increases transparency and helps build stronger relationships, reducing conflicts and making HR technology integration smoother.
Which Outsourcing Strategy Is Right for Your Business?
Deciding between a PEO or HRO (Human Resource Outsourcing) depends on your business’s particular needs, growth targets, market analysis, and how you want to manage operations.
Each choice has its own advantages and potential issues affecting how employees are involved and how HR is handled, influenced by technology integration and market trends. For a deeper insight into such choices, our PEO Comparison Guide: TriNet vs ADP vs Justworks provides a detailed analysis of how different PEOs can meet varying business needs.


